
前言
MyBatis 作为目前最常用的持久层框架之一,分析其源码,对我们的使用过程中可更好的运用它。本系列基于mybatis-3.4.6进行分析。
MyBatis 的初始化工作就是解析主配置文件,映射配置文件以及注解信息。然后保存在org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration,供后期执行数据请求的相关调用。Configuration 里有大量配置信息,在后面每涉及到一个相关配置,会进行详细的分析。
启动
1 | public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { |
分析
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 类
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 的build()是Mybatis启动的初始化入口,使用builder模式加载配置文件。
通过查看该类,使用方法重载,有以下9个方法: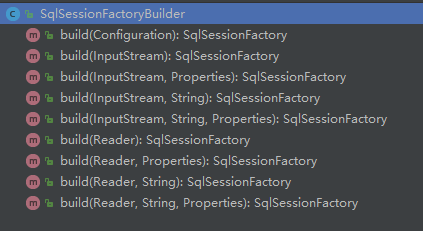
方法重载最终实现处理的方法源码如下:
1 | public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) { |
- environment 是指定加载环境,默认值为 null。
- properties 是属性配置文件,默认值为 null。
同时读取配置文件既可字符流读取,也支持字节流读取。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
实例化 XMLConfigBuilder 类
通过 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 中 XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties), 分析 XMLConfigBuilder实例化过程。
该类中有四个变量:
1 | private boolean parsed; |
- parsed 是否解析,一次解析即可。用于标志配置文件只解析一次,
true为已解析过。 - parser 解析配置的解析器
- environment 加载环境,即
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder中的environment - localReflectorFactory 用于创建和缓存
Reflector对象,一个类对应一个Reflector。因为参数处理、结果映射等操作时,会涉及大量的反射操作。DefaultReflectorFactory实现类比较简单,这里不再进行讲解。
XMLConfigBuilder构建函数实现:
1 | public XMLConfigBuilder(Reader reader, String environment, Properties props) { |
实例化 XPathParser 对象
首先实例化 XPathParser 对象,里面定义了5个变量:
1 | private final Document document; |
- document 保存document对象
- validation xml解析时是否验证文档
- entityResolver 加载dtd文件
- variables 配置文件定义
的值 - xpath Xpath对象,用于对XML文件节点的操作
XPathParser 对象构造函数有: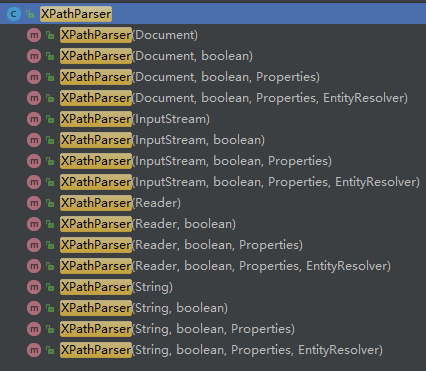
函数里面都处理了两件事:
1 | public XPathParser(Reader reader, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) { |
- 初始化赋值,和创建
XPath对象,用于对XML文件节点的操作。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8private void commonConstructor(boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
this.validation = validation;
this.entityResolver = entityResolver;
this.variables = variables;
// 创建Xpath对象,用于对XML文件节点的操作
XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance();
this.xpath = factory.newXPath();
} - 创建
Document对象并赋值到document变量, 这里属于Document创建的操作,不再详细讲述,不懂可以点击这里查看API1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
// 实例化 DocumentBuilderFactory 对象,用于创建 DocumentBuilder 对象
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// 是否校验文档
factory.setValidating(validation);
// 设置 DocumentBuilderFactory 的配置
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
// 创建 DocumentBuilder
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver);
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
}
});
// 加载文件
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
XMLConfigBuilder构造函数赋值
1 | private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) { |
- 初始化父类
BaseBuilder的值。 - 将外部值赋值给对象。
- 将实例化的
XPathParser赋值给parser。
最后返回XMLConfigBuilder对象。
解析 XMLConfigBuilder 对象
通过 XMLConfigBuilder.parse() 解析配置信息,保存至Configuration。解析详解在后面文章中进行分析。
1 | public Configuration parse() { |
创建 SqlSessionFactory
DefaultSqlSessionFactory实现了SqlSessionFactory接口。
通过上面解析得到的Configuration,调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Configuration config)创建一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory。
1 | public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { |
实例化DefaultSqlSessionFactory的过程,就是将Configuration传递给DefaultSqlSessionFactory成员变量configuration。
1 | public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) { |
创建 SqlSession
通过调用SqlSessionFactory.openSession()创建SqlSession。
1 | public interface SqlSessionFactory { |
- autoCommit 是否自动提交事务,
- level 事务隔离级别(共5个级别), 可查看相关源码
- connection 连接
- execType 执行器的类型:
SIMPLE(不做特殊处理),REUSE(复用预处理语句),BATCH(会批量执行)
因为上面DefaultSqlSessionFactory实现了SqlSessionFactory接口,所以进入到DefaultSqlSessionFactory查看openSession()。
1 | public SqlSession openSession() { |
openSession()方法最终实现代码如下:
1 | private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { |
生成处理器Configuration.newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType):
1 | public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { |
以ExecutorType.SIMPLE为例, BatchExecutor, ReuseExecutor同理: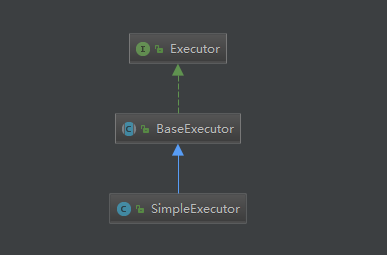
至此,mybatis的启动流程大致简单的介绍到这里,对mybatis的启动初始化有个大致了解。接下将会针对单独模块进行详细分析。


